Adults also need vaccine like children
You’re never too old to get vaccinated!
Adult immunization in India is the most ignored part of heath care services.

Vaccines protects us from many diseases like children adults also need vaccine many diseases are vaccine preventable like hepatitis b, flu, pneumonia, cervical cancer etc
And due to lack of information and not taking vaccine many people are falling sick and even dying with the vaccine preventable diseases.
Vaccines of adults is very important given that >25% of mortality are due to infectious diseases. Vaccines are recommended for adults on the basis of age, prior vaccinations, health conditions, lifestyle, occupation, and travel. There have been significant efforts to curb morbidity, mortality, and disability among adults particularly due to communicable diseases such as tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis, hepatitis A, hepatitis B, human papilloma virus, measles, mumps, rubella, meningococcus, pneumococcus, typhoid, influenza, and chickenpox.
Few vaccines needed by adults are why:
Protection from some childhood vaccines can wear off over time
- Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis
- Viruses and bacteria change over time
- Influenza
- Immune systems tend to weaken over time, putting older adults at higher risk for VPDs
- Influenza, pneumococcus
- Adults with certain chronic or immuno-compromising conditions are more likely to develop complications from certain VPDs 1,2
- Shingles, pneumococcus
- Adults can infect others 3
- Adults who contract measles, mumps or pertussis (whooping cough) can infect infants who may not yet be fully immunized
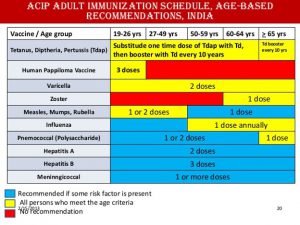
- Administer 1 dose of age-appropriate inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV) or recombinant influenza vaccine (RIV) annually
Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccination
- Administer to adults who previously did not receive a dose of tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap) as an adult or child (routinely recommended at age 11–12 years) 1 dose of Tdap, followed by a dose of tetanus and diphtheria toxoids (Td) booster every 10 years
Measles, mumps, and rubella vaccination
- Administer 1 dose of measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine (MMR) to adults with no evidence of immunity to measles, mumps, or rubella
Administer to adults without evidence of immunity to varicella 2 doses of varicella vaccine (VAR) 4–8 weeks apart if previously received no varicella-containing vaccine (if previously received 1 dose of varicella-containing vaccine, administer 1 dose of VAR at least 4 weeks after the first
Human papillomavirus vaccination
- Administer human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine to females through age 26 years
- The number of doses of HPV vaccine to be administered depends on age at initial HPV vaccination
- Administer 3-dose series at 0, 1–2, and 6 months
- Administer to immunocompetent adults aged 65 years or older 1 dose of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), if not previously administered, followed by 1 dose of 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) at least 1 year after PCV13; if PPSV23 was previously administered but not PCV13, administer PCV13 at least 1 year after PPSV23
- Administer to adults who have a specific risk (see below), or lack a risk factor but want protection, 3-dose series of single antigen hepatitis B vaccine (HepB)
Dr Ruby Bansal, MD, FIHM
HOD preventive Health AND HIV/AIDS
Yashoda superspeciality hospital
Kaushambi, Ghaziabad
Jt. Secretary WOW India